F 14 Vs F 15: Which is the Superior Fighter?
The F-14 Tomcat and the F-15 Eagle are both iconic American fighter aircraft. The F-14, used by the U.S. Navy, is known for its variable-sweep wing design and long-range air-to-air missiles. It excels in fleet defense and can engage multiple targets simultaneously.
The F-15, used by the U.S. Air Force, is a dedicated air superiority fighter with superior maneuverability and acceleration. It can perform sustained high-speed maneuvers and is also capable of ground attack missions. Both aircraft have their strengths, and their effectiveness depends on the mission and the rules of engagement.
What is the Origin of the F-14 Tomcat?
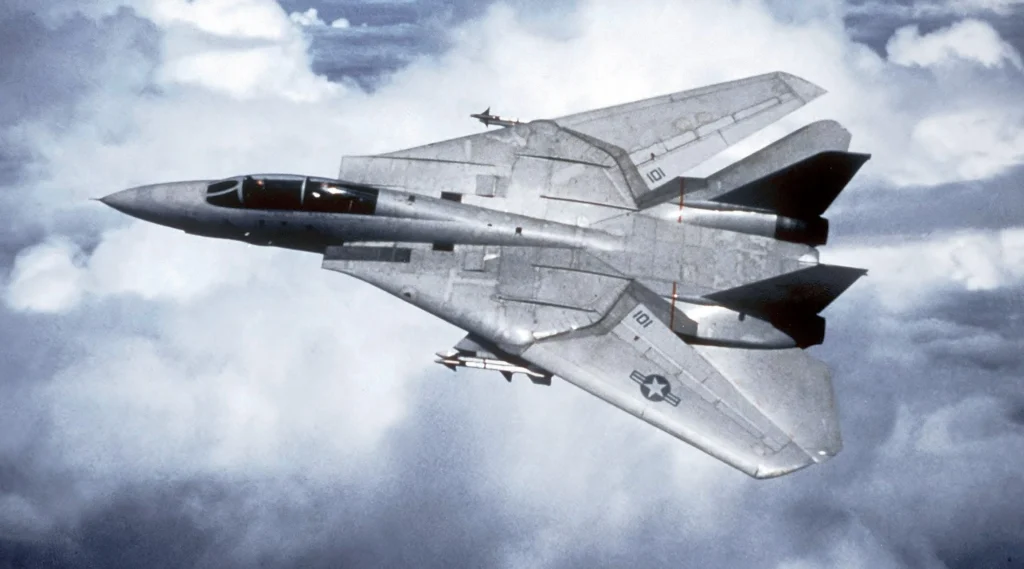

The F-14 Tomcat, or Grumman F-14 Tomcat, stands as a carrier-capable American fighter aircraft. It emerged during the Cold War when the U.S. Navy sought an interceptor to safeguard carrier battle groups from Soviet anti-ship missiles.
Originating in the 1960s, the F-14 was crafted with the aerodynamic and electronic capabilities essential for defending U.S. aircraft-carrier operations against Soviet aircraft and missiles. It was a response to the need created after the discontinuation of the General Dynamics-Grumman F-111B project.
The F-14, part of the “Teen Series” of American fighters, drew inspiration from the lessons learned during the Vietnam War engagements with Soviet MiG designation planes.
Taking its maiden flight on December 21, 1970, the F-14 saw its first deployment in 1974 aboard the USS Enterprise (CVN-65), replacing the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II.
Throughout its service, the F-14 played key roles as the U.S. Navy’s primary maritime air superiority fighter, fleet defense interceptor, and tactical aerial reconnaissance platform until the early 2000s.
In the 1990s, it adopted the Low Altitude Navigation and Targeting Infrared for Night (LANTIRN) pod system, expanding its capabilities to include precision ground-attack missions.
The U.S. Navy retired the F-14 on September 22, 2006, making way for the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet. However, the aircraft continues its service in the Iranian Air Force.
Despite its retirement, the F-14 remains an enduring symbol of American aviation, further cemented by its prominent role in the 1980s blockbuster film “Top Gun.”
How Did the F-15 Eagle Come About?
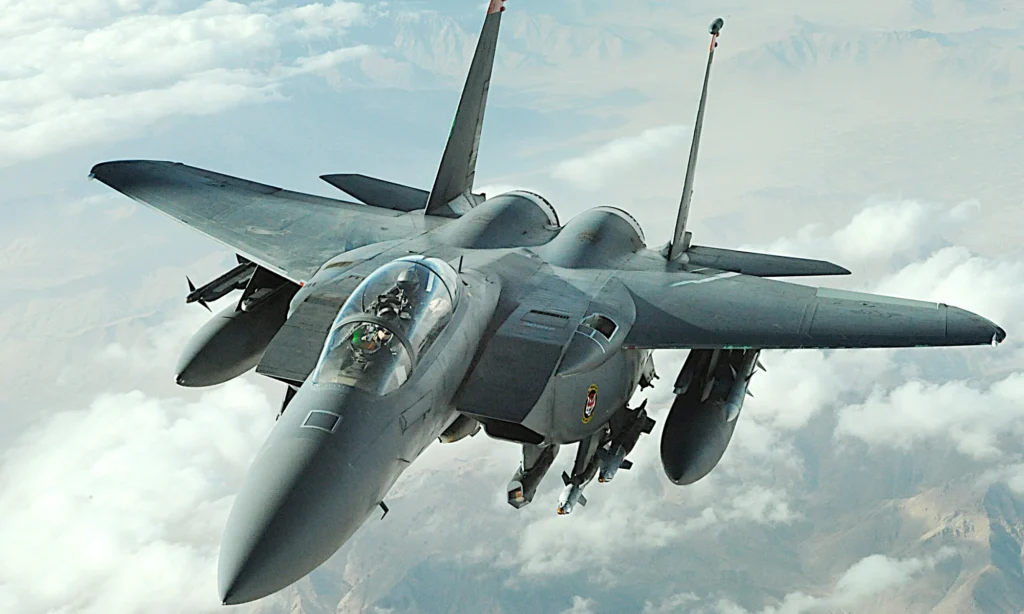

The F-15 Eagle came about as a response to the United States Air Force’s (USAF) need for a high-performance air superiority fighter.
In the late 1960s, the U.S. faced the challenge of developing an aircraft that could counter emerging threats from potential adversaries, particularly those posed by advanced Soviet aircraft. The result was the development of the
McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle, a fourth-generation jet fighter designed to excel in air-to-air combat.
Here is a timeline of the key events in the development of the F-15
Request for Proposals (RFP)
In December 1969, the USAF issued a Request for Proposals (RFP) for a new air superiority fighter. The primary requirements were for a highly maneuverable and fast aircraft with a powerful radar and a large payload capacity.
McDonnell Douglas Wins Contract
McDonnell Douglas won the contract to build the new fighter in December 1969. The company’s design, the F-15, stood out for its impressive combination of speed, range, and advanced avionics.
First Flight
The F-15 prototype took its maiden flight on July 27, 1972. The aircraft demonstrated exceptional agility and performance during testing.
Production and Introduction
The F-15 entered production, and the first operational F-15A Eagles were delivered to the USAF’s Tactical Air Command in 1974.
Advanced Features
The F-15 was equipped with cutting-edge technology, including the powerful AN/APG-63 radar, which provided excellent target detection and tracking capabilities. It also featured a high thrust-to-weight ratio, enabling exceptional climb rates and agility.
Variants and Upgrades
Over the years, various variants of the F-15 were developed, including the two-seat F-15B, the ground-attack-focused F-15E Strike Eagle, and the upgraded F-15C and F-15D models. The aircraft underwent continuous upgrades to maintain its technological edge.
Combat Success
The F-15 has seen extensive service in the U.S. Air Force and has been widely exported to allied nations. It has an impressive combat record and is known for its air superiority capabilities.
What are the Design and Features of the F-14 Tomcat?
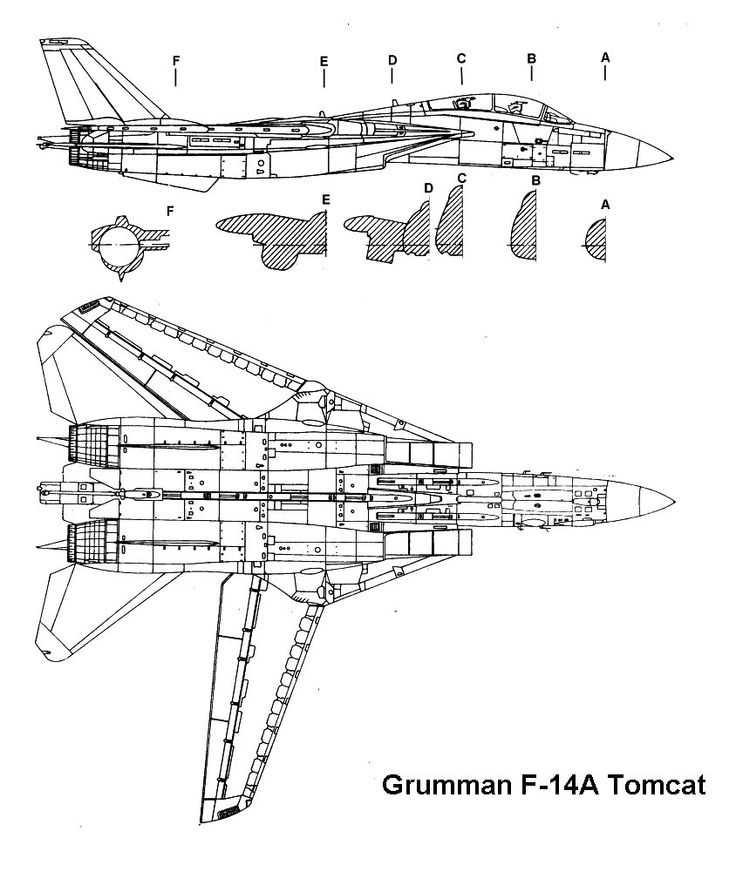
The F-14 Tomcat, a carrier-capable fighter aircraft, was designed to be a versatile and powerful platform, incorporating several distinctive features. Here are the key design elements and features of the F-14 Tomcat:
Variable-Sweep Wing
One of the most notable features of the F-14 is its variable-sweep wing design. This allows the wings to be swept back during high-speed flight for improved aerodynamics and swept forward for lower-speed and carrier operations.
Twin-Engine Configuration
The F-14 is powered by two turbofan engines, providing the necessary thrust for supersonic speeds and maneuverability. The original engines were the Pratt & Whitney TF30, later replaced by the General Electric F110 in some variants.
Two-Seat Configuration
The F-14 is a two-seat aircraft, with a pilot and a radar intercept officer (RIO). This two-seat arrangement enhances the operational capabilities of the aircraft, allowing for effective radar operation, weapon employment, and mission management.
Twin-Tail Configuration
The F-14 features a twin-tail design, with two vertical stabilizers at the rear of the aircraft. This design contributes to the aircraft’s stability and control during flight.
All-Weather Capability
The F-14 was designed to operate in all weather conditions, providing the U.S. Navy with a versatile aircraft capable of performing missions in various environments.
Advanced Avionics
The F-14 was equipped with advanced avionics, including radar systems such as the AN/AWG-9, which was capable of long-range target detection and tracking. The radar was a key component for the F-14’s air-to-air combat capabilities.
Phoenix Missile System
The F-14 was designed to carry the AIM-54 Phoenix, a long-range air-to-air missile with the capability to engage multiple targets simultaneously. This missile system was a significant aspect of the F-14’s role as a fleet defense interceptor.
Multi-Role Capabilities
While originally designed for air superiority missions, the F-14 evolved to have multi-role capabilities. It could perform tasks such as fleet defense, tactical reconnaissance, and ground-attack missions with the addition of systems like the Low Altitude Navigation and Targeting Infrared for Night (LANTIRN) pod.
Catapult Launch and Arrested Landing
Being carrier-capable, the F-14 could take off from and land on aircraft carriers using catapults for takeoff and arresting gear for landing.
High-Visibility Cockpit
The cockpit design of the F-14 provided good visibility for the crew, facilitating situational awareness during missions.
What Makes the F-15 Eagle Unique?

The McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle, an American twin-engine tactical fighter aircraft designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing), stands out in various aspects
Design and Aerodynamics
The F-15 is a twin-engine, twin-tail fighter jet recognized for its substantial size and impressive aerodynamics. Its design incorporates a powerful radar, advanced avionics, and a spacious cockpit for the pilot. The airframe is designed to carry a significant amount of fuel, providing the F-15 with exceptional range and endurance.
Performance and Air Superiority
The F-15 Eagle is an all-weather tactical fighter celebrated for its exceptional maneuverability and designed to secure air supremacy over the battlefield. Its performance is a result of unmatched maneuverability, acceleration, range, weaponry, and avionics. The aircraft can penetrate enemy defenses, surpass and outfight contemporary enemy aircraft.
Avionics and Electronic Systems
Equipped with advanced avionics, the F-15 boasts electronic systems and weaponry for detecting, acquiring, tracking, and attacking enemy aircraft in various airspace conditions. Its weapons and flight control systems are designed for single-pilot air-to-air combat effectiveness.
Superior Maneuverability and Acceleration
The F-15’s superior maneuverability and acceleration are achieved through a high engine thrust-to-weight ratio and low wing-loading. This combination allows the aircraft to execute tight turns without sacrificing airspeed.
Multi-Mission Avionics System
Setting it apart, the F-15 features a comprehensive multi-mission avionics system, including a head-up display, advanced radar, inertial navigation system, flight instruments, ultrahigh frequency communications, tactical navigation system, and instrument landing system. It also incorporates internally mounted tactical electronic warfare systems, an “identification friend or foe” system, electronic countermeasures, and a central digital computer.
Combat Record
The F-15 has earned distinction as one of the most successful modern fighters, boasting a combat record of over 100 victories and no losses in aerial combat, predominantly attributed to the Israeli Air Force.
Versatility
Originally designed for air superiority, the F-15’s versatility became evident with its secondary ground-attack capability. This adaptability led to the development of the F-15E Strike Eagle, an improved all-weather strike derivative that entered service in 1989 and has since been exported to several nations.
Performance and Capabilities
The F-14 Tomcat is a unique aircraft designed for fleet defense, capable of engaging multiple targets simultaneously at long range. Its variable-sweep wing design allows it to excel in a variety of mission profiles. The F-14 can reach a top speed of Mach 2.34, equivalent to 1,544 mph or 2,485 km/h at high altitude.
This speed is largely due to the aircraft’s variable-sweep wing design and the raw power output of its TF30-P-414A engines with afterburners engaged. The F-14 often flew at a normal cruising speed to reduce fuel consumption.
During its development, the F-14 saw upgrades to its Phoenix, Sparrow, and Sidewinder missiles, making it more lethal. Testing resulted in a Phoenix kill at 200 km and an 80% success rate in a rapid-fire Phoenix volley.
On the other hand, the F-15 Eagle, as a dedicated air superiority fighter, excels in aerial combat. It has a superior thrust-to-weight ratio, allowing it to perform sustained high-speed maneuvers. The F-15 Eagle is powered by two Pratt & Whitney F100-PW229 engines, each producing 29,000 pounds of thrust.
This gives the aircraft enough power to reach speeds up to Mach 2.5 and altitudes above 65,000 feet. It has a maximum take-off weight (MTOW) of 51,158 pounds and a maximum payload capacity of 13,600 pounds. The F-15’s superior maneuverability and acceleration are achieved through high engine thrust-to-weight ratio and low wing-loading.
Low wing-loading (the ratio of aircraft weight to its wing area) is a vital factor in maneuverability and, combined with the high thrust-to-weight ratio, enables the aircraft to turn tightly without losing airspeed. The F-15 is also capable of ground attack missions. It proved flexible enough that an improved all-weather strike derivative, the F-15E Strike Eagle, was later developed, entered service in 1989, and has been exported to several nations.
FAQ
Why was the F-14 retired but not the F-15?
The F-14 was phased out in favor of the more versatile F/A-18, which, while less powerful, could fulfill multiple roles. The F-14 was succeeded by a project that had already been in development for 16 years in 2006 — the F/A-18 was a project of the 80’s — but the F-15 continues to operate alongside the F-22.
Is the F-14 better than the F18?
The F-14 is significantly faster and more powerful than the F/A-18, with a top speed of 2.34 Mach, while the Super Hornet reaches Mach 1.8. However, the F/A-18 has more complex electronic systems.
Which is better F-15 or F-16?
Both the F-15 and F-16 are high-performance aircraft. The F-15 has greater durability and stronger air-to-air combat capabilities than the F-16 due to its heavy armor and upgraded avionics systems. However, the F-16 is smaller, making it harder to visually detect and having a tighter instantaneous turn radius, while the F-15 is faster and recovers faster due to a higher thrust to weight ratio.
Is Rafale better than F-16?
The Rafale can carry a larger payload than the F-16. Both can carry nuclear warheads when necessary. The area where Rafale falls short is its range, which is significantly less than that of the F-16.
Is F22 faster than F-15?
The F-22 has a top speed of Mach 2.2, which is slightly slower than the F-15.
Is F 18 faster than F-15?
The F-16 has a top speed of Mach 2.0, while the F/A-18 can only reach Mach 1.8.
Is the SU 35 better than F-22?
The Su-35 is larger, faster, and has a longer range than the F-22. However, the F-22 is nearly undetectable and can lock onto a target without being in visual range.
Has the F-15 lost?
According to official releases from Boeing and the U.S. Air Force, the F-15 Eagle has a clear-cut win-to-loss ratio of 104 to zero. However, opposing air forces have claimed, in nearly a dozen cases, to have shot down the iconic, twin-engine fighter.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, both the F-14 Tomcat and the F-15 Eagle are iconic American fighter aircraft, each with its own strengths and operational requirements. The F-14, known for its variable-sweep wing design and long-range air-to-air missiles, excels in fleet defense.
On the other hand, the F-15, a dedicated air superiority fighter, is known for its superior maneuverability and acceleration. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these aircraft largely depends on the mission and the rules of engagement.
While the F-14 has been retired by the U.S. Navy, the F-15 continues to serve in the U.S. Air Force and other air forces around the world. Both aircraft have left a significant mark in the history of aviation.







